Vector is a geometrical entity used in Computational Geometry, which has magnitude and direction.
Computational Geometry Library in Python – Vector:
class CGLibPy_Vector(object):
I = 0.0
J = 0.0
K = 0.0
vecLen = 0.0
def __init__(self,_args):
if len(_args) == 3: # Three Coefficients
self.I = _args[0]
self.J = _args[1]
self.K = _args[2]
elif len(_args) == 2: # Six Coordinates
self.I = _args[1].X - _args[0].X
self.J = _args[1].Y - _args[0].Y
self.K = _args[1].Z - _args[0].Z
self.vecLen = math.sqrt(self.I*self.I + self.J*self.J + self.K*self.K)
def normalize(self):
self.I = self.I/self.vecLen
self.J = self.J/self.vecLen
self.K = self.K/self.vecLen
If a vector is defined by two point A and B then, vector direction is determined using coordinates of A and B. The magnitude of vector is determined by distance between in A and B.
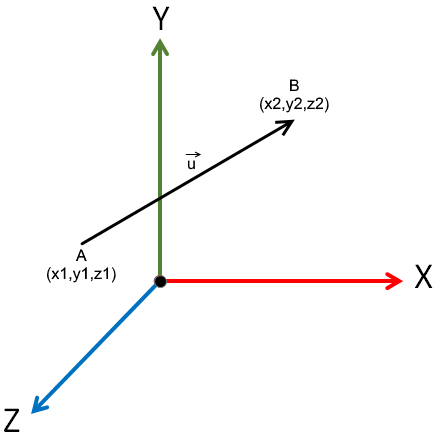
→
u is defined as direction vector where,
u = (x2-x1)i + (y2-y1)j + (z2-z1)k
where, i, j and k are Unit Vectors along X,Y and Z axis respectively. Units Vectors are vectors whose magnitude is One (1). Any vector can be converted into Unit Vector by dividing each component of the vector by magnitude. So, if a vector is given as,
V = ai + bj +ck
Magnitude of vector = |AB| = √a2 + b2 + c2
and
Unit Vector = (a/|AB|)i + (b/|AB|)j + (c/|AB|)k
This process of converting a vector into a unit vector is known as Normalization of vector.
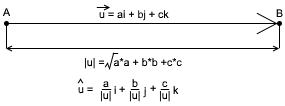
Properties of vectors:
- Vectors are equal if magnitudes and directions are same
- Two vectors are parallel if they are in same or opposite direction